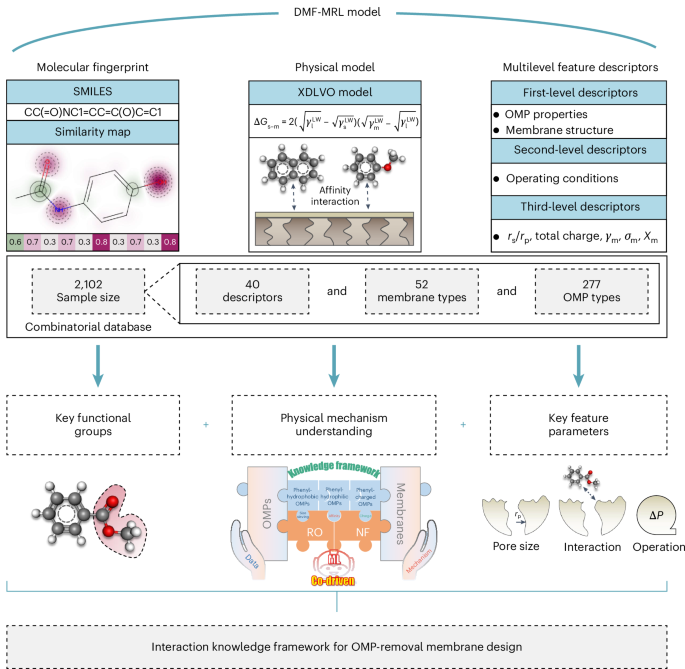
A smart framework to design membranes for organic micropollutants removal
Christou, A. et al. Sustainable wastewater reuse for agriculture. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 5, 504–521 (2024).
Google Scholar
Alsbaiee, A. et al. Rapid removal of organic micropollutants from water by a porous β-cyclodextrin polymer. Nature 529, 190–194 (2016).
Google Scholar
Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality 4th edn (WHO, 2022); https://www.who.int/teams/environment-climate-change-and-health/water-sanitation-and-health/water-safety-and-quality/drinking-water-quality-guidelines
Shannon, M. et al. Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nature 452, 301–310 (2008).
Google Scholar
Yao, Y. et al. High performance polyester reverse osmosis desalination membrane with chlorine resistance. Nat. Sustain. 4, 138–146 (2021).
Huang, J. et al. Polymeric membranes with highly homogenized nanopores for ultrafast water purification. Nat. Sustain. 7, 901–909 (2024).
Lu, D. et al. Separation mechanism, selectivity enhancement strategies and advanced materials for mono-/multivalent ion-selective nanofiltration membrane. Adv. Membr. 2, 100032 (2022).
Liang, Y. et al. Polyamide nanofiltration membrane with highly uniform sub-nanometer pores for sub-1 Å precision separation. Nat. Commun. 11, 2015 (2020).
Google Scholar
Tan, Z. et al. Polyamide membranes with nanoscale Turing structures for water purification. Science 360, 518–521 (2018).
Google Scholar
Giorno, L. Membranes that filter and destroy pollutants. Nat. Nanotechnol. 17, 334–335 (2022).
Google Scholar
Liu, Y. L. et al. Exploring the interactions of organic micropollutants with polyamide nanofiltration membranes: a molecular docking study. J. Membr. Sci. 577, 285–293 (2019).
Google Scholar
Guo, H. et al. Does hydrophilic polydopamine coating enhance membrane rejection of hydrophobic endocrine-disrupting compounds? Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 3, 332–338 (2016).
Google Scholar
Zha, Z. et al. Interlayer-modulated polyamide composite membrane for organic solvent nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 647, 120306 (2022).
Google Scholar
Wang, P. et al. Strong improvement of nanofiltration performance on micropollutant removal and reduction of membrane fouling by hydrolyzed-aluminum nanoparticles. Water Res. 175, 115649 (2020).
Google Scholar
Khoo, Y. S. et al. Removal of emerging organic micropollutants via modified-reverse osmosis/nanofiltration membranes: a review. Chemosphere 305, 135151 (2022).
Google Scholar
Ratchnashree, S. R. et al. Advanced technologies for the determination of quantitative structure-activity relationships and degradation efficiency of micropollutants and their removal in water—a review. Sci. Total Environ. 904, 166563 (2023).
Google Scholar
Lin, Y. L. et al. Improving the organic and biological fouling resistance and removal of pharmaceutical and personal care products through nanofiltration by using in situ radical graft polymerization. Sci. Total Environ. 635, 543–550 (2018).
Google Scholar
Ma, X. et al. Revealing key structural and operating features on water/salts selectivity of polyamide nanofiltration membranes by ensemble machine learning. Desalination 548, 116293 (2023).
Google Scholar
Ritt, C. L. et al. Machine learning reveals key ion selectivity mechanisms in polymeric membranes with subnanometer pores. Sci. Adv. 8, eabl5771 (2022).
Google Scholar
Priya, P. et al. Machine learning assisted screening of two-dimensional materials for water desalination. ACS Nano 16, 1929–1939 (2022).
Google Scholar
Zhu, T. Y. et al. Prediction of organic contaminant rejection by nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes using interpretable machine learning models. Sci. Total Environ. 857, 159348 (2023).
Google Scholar
Jeong, N. et al. Exploring the knowledge attained by machine learning on ion transport across polyamide membranes using explainable artificial intelligence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 57, 17851–17862 (2023).
Google Scholar
Tayara, A. et al. Machine learning models for predicting the rejection of organic pollutants by forward osmosis and reverse osmosis membranes and unveiling the rejection mechanisms. Water Res. 266, 122363 (2024).
Google Scholar
Hu, A. et al. A machine learning based framework to tailor properties of nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes for targeted removal of organic micropollutants. Water Res. 268, 122677 (2025).
Google Scholar
Jeong, N. et al. Elucidating governing factors of PFAS removal by polyamide membranes using machine learning and molecular simulations. Nat. Commun. 15, 10918 (2024).
Google Scholar
Wang, H. J. et al. Understanding rejection mechanisms of trace organic contaminants by polyamide membranes via data-knowledge codriven machine learning. Environ. Sci. Technol. 58, 5878–5888 (2024).
Google Scholar
Wang, M. et al. Accelerating discovery of high fractional free volume polymers from a data-driven approach. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14, 31203–31215 (2022).
Google Scholar
Mahlangu, T. O. et al. Role of permeate flux and specific membrane-foulant-solute affinity interactions (∆Gslm) in transport of trace organic solutes through fouled nanofiltration (NF) membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 518, 203–215 (2016).
Google Scholar
Wang, R. et al. Pore model for nanofiltration: history, theoretical framework, key predictions, limitations, and prospects. J. Membr. Sci. 620, 118809 (2021).
Google Scholar
Jeong, N. et al. Predicting micropollutant removal by reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes: is machine learning viable? Environ. Sci. Technol. 55, 11348–11359 (2021).
Google Scholar
Liu, Y. L. et al. Boosting the performance of nanofiltration membranes in removing organic micropollutants: trade-off effect, strategy evaluation, and prospective development. Environ. Sci. Technol. 56, 15220–15237 (2022).
Google Scholar
Breitner, L. N. et al. Effect of functional chemistry on the rejection of low-molecular weight neutral organics through reverse osmosis membranes for potable reuse. Environ. Sci. Technol. 53, 11401–11409 (2019).
Google Scholar
Dan, L. et al. Ensemble machine learning reveals key structural and operational features governing ion selectivity of polyamide nanofiltration membranes. Desalination 564, 116748 (2023).
Lesovoy, D. M. et al. NMR relaxation parameters of methyl groups as a tool to map the interfaces of helix–helix interactions in membrane proteins. J. Biomol. NMR 69, 165–179 (2017).
Google Scholar
Heiranian, M. et al. Mechanisms and models for water transport in reverse osmosis membranes: history, critical assessment, and recent developments. Chem. Soc. Rev. 52, 8455–8480 (2023).
Google Scholar
Wang, L. et al. Water transport in reverse osmosis membranes is governed by pore flow, not a solution-diffusion mechanism. Sci. Adv. 9, eadf8488 (2023).
Google Scholar
Wang, F. F. et al. Experiments and machine learning-based modeling for haloacetic acids rejection by nanofiltration: influence of solute properties and operating conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 883, 163610 (2023).
Google Scholar
Lin, S. S. et al. A zwitterion-like, charge-balanced ultrathin layers on polymeric membranes for antifouling property. Environ. Sci. Technol. 52, 4457–4463 (2018).
Google Scholar
Niu, C. et al. Artificial intelligence-incorporated membrane fouling prediction for membrane-based processes in the past 20 years: a critical review. Water Res. 216, 118299 (2022).
Google Scholar
Liang, L. et al. Machine learning in membrane science: bridging materials, structures, and performance for next-generation membrane design. Sep. Purif. Technol. 369, 133091 (2025).
Google Scholar
Gao, H. et al. Revolutionizing membrane design using machine learning Bayesian optimization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 56, 2572–2581 (2022).
Google Scholar
Cao, Z. et al. Machine learning in membrane design: from property prediction to AI-guided optimization. Nano Lett. 24, 2953–2960 (2024).
Google Scholar
Donnan, F. G. Theory of membrane equilibria and membrane potentials in the presence of non-dialysing electrolytes. A contribution to physical-chemical physiology. J. Membr. Sci. 100, 45–55 (1995).
Google Scholar
Van Oss, C. J. Acid—base interfacial interactions in aqueous media. Colloids Surf. A 78, 1–49 (1993).
Kima, S. et al. Interactions controlling biopolymer fouling of reverse osmosis membranes. Desalination 202, 333–342 (2007).
Subramani, A. et al. Direct observation of initial microbial deposition onto reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 319, 111–125 (2008).
Google Scholar
Guo, J. et al. Temperature dependency of the apolar surface tension component for water and its role in classifying apolar and polar interfacial interactions. J. Phys. Chem. C 127, 18167–18175 (2023).
Google Scholar
link